Introduction
Documentation is an important part of our personal, professional, and organizational life. There are many types of documents and they are all used in every sector across the world, from legal documents to healthcare documents, to software documents, etc. Documentation, especially proper documentation, will never be a bad thing and we can state that it automates processes, and ensures compliance, accountability, and transparency.
This guide covers in detail the types of documentation, their uses, and best practices on how to design and maintain them in the domains of ERP, financial, legal, healthcare, and software development. Personal documents, official documents, or even any records that relate to the industry could either help you sail or hinder you from the eighth gear while making a decision.
What is Documentation?
Documentation means an organized collection and storage of information in any written, visual, or digitally structured format. It guarantees that Data, Processes, or Procedures are systematically documented in order to be accessible or referred to when needed.
Why is Documentation Important?
- Accountability: Information by itself does not penalize people or organizations for what they do. Documentation does.
- Compliance: Many industries need proper documentation to meet regulatory needs.
- Efficiency: Streamlined documentation, results in faster time to market and a reduction in errors.
- Preservation: Documentation is important, it saves vital information for future use.
Types of Documentations:
There are three parts of documentation; personal documents, official documents, and industry-specific documentation. Further down, we’ll break it down as we delve into the most common document types and their importance.
1. Personal Documents
Personal documents are records that an individual keeps for private (or personal), legal, or financial reasons. These include identification papers, financial statements,s, and medical records.
Key Examples:
- Identification Documents: Passports driver’s licenses and birth certificates.
- Educational Records: Degrees, certifications, and transcripts.
- Medical Records: Prescriptions, Health reports, and vaccination cards.
- Financial Documents: Credit reports, tax returns, and bank statements.
Importance:
It helps in identity establishment, like: who are you? Can you get services without documents? Proof of identity makes things like paying taxes, opening a bank account, or working legally.
2. Official Documents
And they are records issued by governmental or institutional bodies. For administrative processes, these documents are often legally binding.
Key Examples:
- Legal Documents: Affidavits, court orders, etc., Contracts.
- Employment Documents: ETS may also give employees offer letters, employment contracts, and, when they leave, termination letters.
- Government-issued documents: Voter IDs, permits, and social security cards.
Importance:
They are record-keeping documents; they provide authenticity and are used for proving agreements/ rights or responsibilities etc.
3. Healthcare Documentation
Healthcare Documentation tells the story of a patient’s encounter with the healthcare system is important for providing continuity to treatment plans and tracking medical history. Clinical and administrative records are in this category.
Key Examples:
- Patient Records: Diagnostic reports, treatment plans, and medical histories.
- Insurance Documentation: Claims, policy details, and reimbursement records.
- Compliance Reports: HIPAA and other regulatory standards records.
Importance:
Good documentation of patient care guarantees proper diagnosis, efficacious treatment, and adherence to health care regulations.
4. Financial Documentation
Financial documentation includes the record of income, expenses, and financial transactions. Accurate financial records are really important both for individuals and organizations.
Key Examples:
- Invoices and Receipts: Proof of transactions.
- Balance Sheets: These are accounts of assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Tax Documentation: TDS certificates, Audit reports, and Tax Returns.
Importance:
Financial documentation is useful for budgeting, compliance with tax, and making decisions.
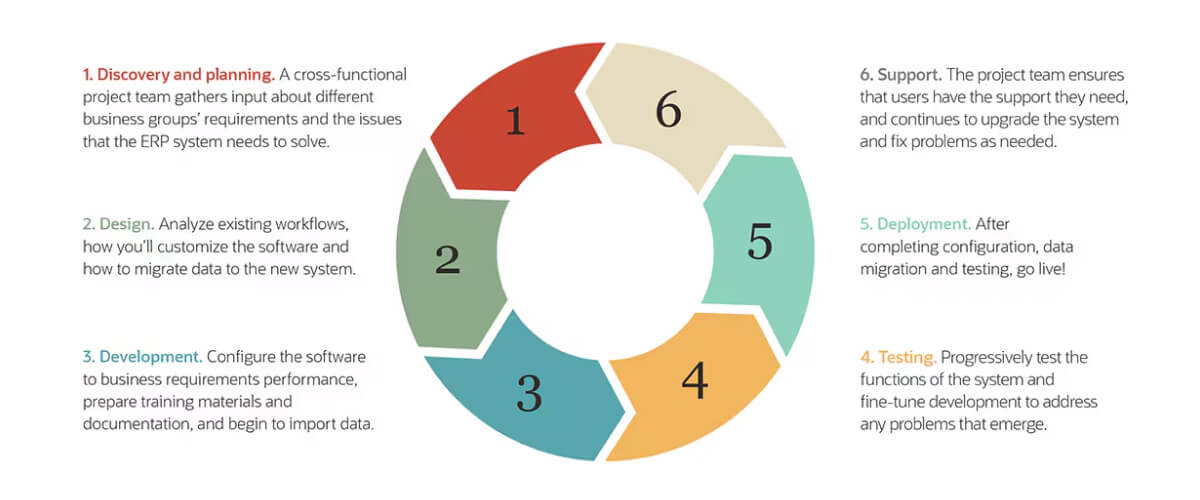
5. ERP Documentation
Documentation is important for business processes to be processed quickly and effectively in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. System setup, maintenance, and training require ERP documentation.
Key Examples:
- User Manuals: ERP software guides you on how to navigate.
- Configuration Documents: Documentation of system setup and customizations.
- Process Flowcharts: Workflows visual representations.
- Training Materials: Onboarding employee’s documentation on ERP systems.
Importance:
ERP documentation is used to implement ERP smoothly, operate it effectively, and with minimal impact on operations during transitions.
6. Legal Documentation
Legal documentation is important in determining the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of legal documentation. These documents are, however, often enforceable by law.
Key Examples:
- Contracts: The agreements between two or more parties.
- Property Documents: Leases, deeds, and mortgage papers.
- Corporate Legal Records: Articles of incorporation, shareholder agreements, and compliance reports.
Importance:
The documents make things clear and protect the interests of everyone.
7. Software Development Documentation
To aid in clarity and teamwork on software development projects is extensive documentation needed.
Key Examples:
- Business Requirements Documents (BRD): They define the project goal and determine the business outcome.
- Technical Design Documents (TDD): Describe system architecture and technical specifications.
- User Manuals: They are given instructions that end users need to follow.
- Code Documentation: Provide an explanation of the logic and the functionality of the codebase.
Importance:
In software development documentation is truly an afterthought and it makes collaboration less effective, increases errors and leads to maintaining difficult web applications and code.
8. Educational Documentation
In academic settings, educational documentation lends support to learning, research, and administration.
Key Examples:
- Curriculum Guides: Courses and programs have detailed plans.
- Research Papers: The storing of studies and the findings, formally documented on them.
- Student Records: Information, such as grades and whose classes the student attends.
Importance:
These documents guarantee effective learning and administrative efficiency.
9. Project Management Documentation
Project Management Documentation is written to plan, execute, and [monitor] the progress of the project effectively.
Key Examples:
- Project Proposals: Identify project objectives, scope; timelines.
- Gantt Charts: Visualize project schedules.
- Risk Assessments: Highlight and counter the risks that might have been caused by the project.
- Minutes Of Meeting: Conduct record discussions and record decisions.
Importance:
Project Management documentation is used in project management to keep the stakeholders aligned and on track to fulfill the objectives timely.
10. Research Documentation
Scientific and academic research documentation is essential for preserving data, methodologies, and findings.
Key Examples:
- Proposals: Describe the research hypothesis and methodology.
- Laboratory Notes: Observe and make a record of configurations that were set up in the experimental room.
- Final Reports: Present summary of findings and conclusions.
Importance:
Done on a note, the research is well documented for reproducibility and credibility.
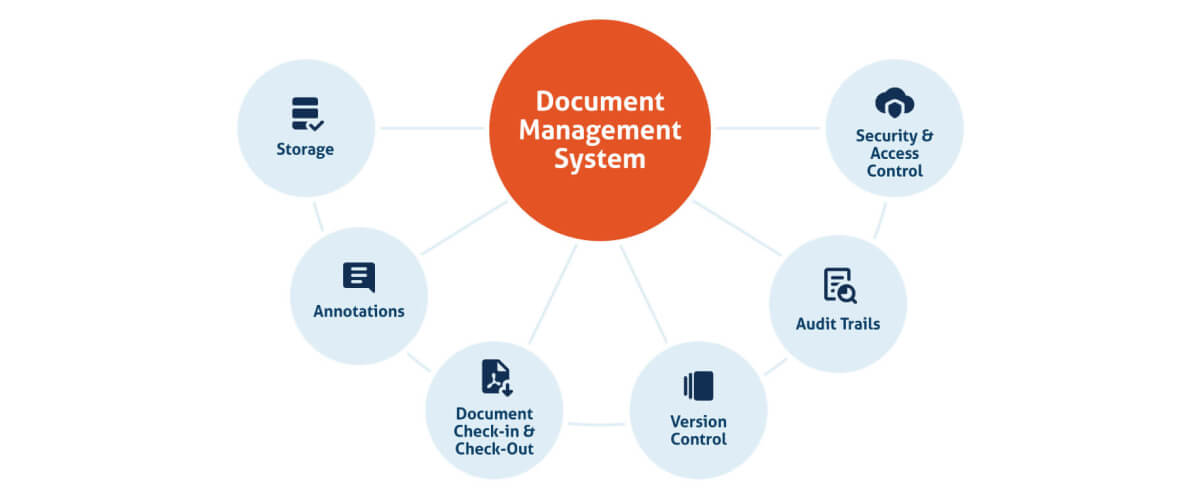
Document Management: Best Practices
The ability to produce and maintain documentation efficiently can make a big difference in how it is utilized. Below are some best practices for document management:
1. Use Standardized Formats
Keep all types of documentation in a similar standard template and format to keep it consistent.
2. Implement Version Control
Lower maintenance keys may in turn lead to using some kind of track changes with version history tools such as Git or dedicated document management systems.
3. Ensure Accessibility
Centralized repository for storage of the documents where authorized people can easily access them.
4. Maintain Data Security
Encrypt files, protect with access controls and monitor regularly.
5. Automate Processes
Use ERP systems, Doc management software, or AI-powered tools to document faster.
Conclusion
Documentation goes far beyond record keeping and can be a driver of efficiency, accountability, and compliance throughout much of the industries. The basic idea of getting to know the various types of documentation like personal documents, legal documents, ERP documents, and many more, will help people and organizations manage information properly. This is why as an organization you need to adopt best practices for document management so your documentation can be accurate, accessible, and secure.
FAQs
1. What is the importance of documentation?
Documentation improves communication, it improves compliance and it helps to perform tasks efficiently. It serves as a trustworthy basis for all personal, legal, and professional activities.
2. What are the most common types of documentation?
Some of the common types of documents are as follows:
- personal documents.
- Official documents.
- Legal documents.
- Healthcare documentation.
- Software development documentation.
3. How can I improve document management?
You can normalize using templates, use version control, make documents accessible to everyone, protect the data security, and automate completing repetitive tasks with document management tools.
4. What tools are used for documentation?
The most common such tools are Microsoft Word, Google Docs, Notion, Confluence, Git, and, in some organizations, document management systems such as DocuWare.
5. Why is legal documentation important?
Legal documentation provides enforceable agreements and establishes the rights and responsibilities of the parties along with clarity from disputes.